New Study Proves AI Can Improve Early Breast Cancer Detection
In a groundbreaking real-world study, researchers have demonstrated that integrating artificial intelligence into breast cancer screening significantly enhances detection rates. This marks the first large-scale deployment of AI in a national screening program, providing valuable insights into its potential to revolutionize early cancer diagnosis.
For years, studies have indicated that AI could aid medical professionals in identifying cancers by detecting abnormalities in CT scans and spotting signs of breast cancer in mammograms. However, most studies until now have been retrospective. Many have also been limited by small sample sizes. This has left a gap in understanding AI’s efficacy in real-world clinical settings.
A Nationwide Study
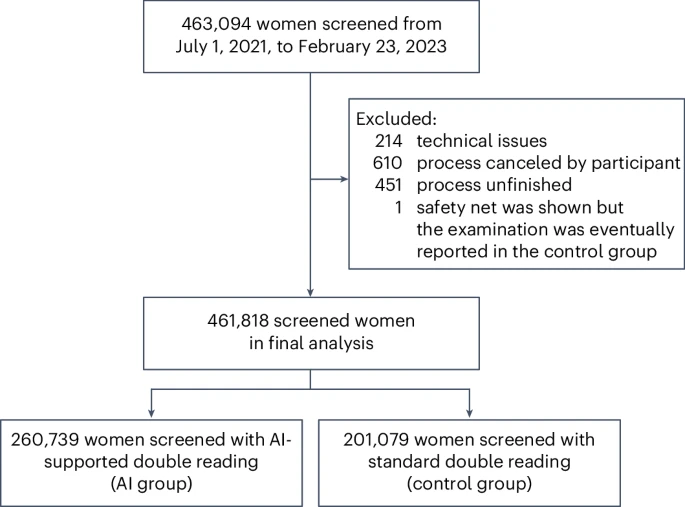
The research, conducted as part of Germany’s national breast cancer screening program, analyzed data from 461,818 women aged 50–69 who participated between July 2021 and February 2023. All scans were independently reviewed by two radiologists. However, for 260,739 women, at least one radiologist used an AI tool for additional support.
The AI tool performed two critical functions. First, it labeled scans deemed unsuspicious as “normal.” Then, it issued “safety net” alerts for scans it flagged as suspicious but were considered normal by the radiologist. These alerts highlighted specific areas for further review.
Enhanced Detection with Minimal Risk
The study revealed that the AI-assisted group achieved a breast cancer detection rate that was 17.6% higher than the standard group, equating to one additional cancer diagnosis per 1,000 women screened. Importantly, this improvement did not lead to a higher rate of false positives. The recall rate for further investigation remained consistent across both groups.
Professor Alexander Katalinic from the University of Lübeck emphasized that the integration of AI enhanced detection rates without increasing harm for participants. He stated:
“This is a better result, with the same harm.”
AI as a Safety Net
The AI tool’s safety net feature played a pivotal role in preventing missed diagnoses. In the AI-assisted group, this feature was triggered 3,959 times, leading to 204 confirmed breast cancer cases. Without this safeguard, 20 cancers in the AI group could have been overlooked. This highlights the system’s value in complementing radiologists’ expertise.
Stefan Bunk, co-founder of Vara, the company behind the AI tool, noted that the technology streamlined the review process for scans labeled as “normal.” He added that even without expert review, overall detection rates would remain higher. This would result in fewer false positives and reduced workloads for radiologists.
Expert Perspectives
The findings have garnered widespread attention and praise from experts, with Stephen Duffy, emeritus professor of cancer screening at Queen Mary University of London, calling the results “credible and impressive.” He highlighted the potential for AI to replace the need for two radiologists in settings like the UK. In the UK, radiologist shortages are a pressing concern.
However, some experts raised cautionary notes. Dr. Kristina Lång of Lund University acknowledged the study’s encouraging results but warned about the increase in detected in situ cancers, which may contribute to overdiagnosis. She said:
“Long-term follow-up is essential to fully understand the clinical implications of integrating AI into mammography screening.”
Similarly, Dr. Katharine Halliday, president of the Royal College of Radiologists, stressed the importance of careful implementation. She noted the 29% shortfall of radiologists in the NHS. While AI tools can boost accuracy and productivity, she emphasized that expert oversight is crucial to mitigate potential risks.
A Promising Step Forward
This study marks a breakthrough in integrating AI into routine breast cancer screening. It boosts detection rates, eases radiologists’ workloads, and tackles resource shortages in global healthcare.
Yet, experts stress the need for rigorous research and long-term follow-up to ensure AI’s benefits translate into better patient outcomes. The journey is just beginning, but AI’s transformative potential is unmistakable.