The Top Scientific Breakthroughs of 2024

As we bid farewell to 2024, it’s time to reflect on the remarkable scientific advancements and breakthroughs that have defined the year. From groundbreaking discoveries in space exploration to transformative innovations in medicine and technology, 2024 has been a landmark year for science. This article highlights the most significant events, organized month by month.
January 2024: A Promising Start
2 January: The Japan Meteorological Agency confirmed 2023 as the warmest year on record globally.
3 January: Scientists created the first functional semiconductor made from graphene, paving the way for faster and more efficient electronic devices.
13 January: NASA opened the Bennu asteroid sample container, offering insights into the early solar system’s formation.
17 January: A newly discovered hormone, Glycogenin-2, was linked to improved glucose metabolism, sparking hope for new diabetes treatments.
19 January: Japan achieved the fifth successful soft landing on the Moon, continuing humanity’s exploration of our closest celestial neighbor.
24 January: The Large Hadron Collider reported new evidence of tetraquarks, expanding our understanding of particle physics.
31 January: NASA discovered a super-Earth, TOI-715 b, located in the habitable zone, reigniting discussions about extraterrestrial life.
February 2024: Pioneering Solutions
2 February: Researchers proposed a potential solution to the longstanding three-body problem, a major breakthrough in astrophysics.
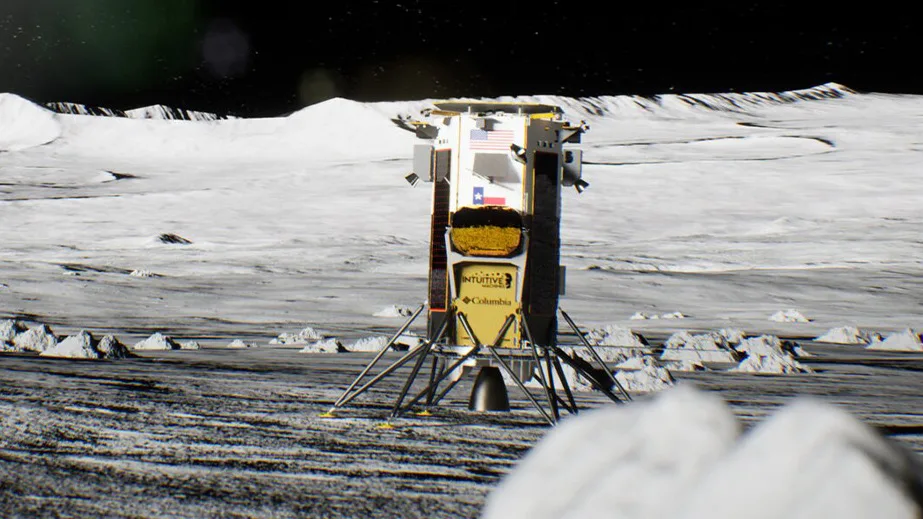
22 February: Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lander became the first commercial vehicle to land on the Moon, marking a milestone in private space exploration.
26 February: Prebiotic resistant starch was shown to aid weight loss in small trials, offering new avenues for combating obesity.
March 2024: Quantum Leaps and Medical Marvels
4 March: Europa, Jupiter’s moon, may have less oxygen than previously thought, challenging its potential for life.
Biochemists create an RNA molecule capable of making accurate copies, supporting the RNA world hypothesis.
6 March: Colossal Biosciences creates the first induced pluripotent stem cells for the Asian elephant, a step toward woolly mammoth de-extinction.
13 March: The EU passes the world’s first comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Act.
14 March: SpaceX successfully launches Starship, but the rocket fails upon re-entry.
19 March: Scientists demonstrate a wireless brain-sensing network of 78 sensors.
26 March: A study proposes ecological pandemic prevention measures for policy frameworks.
28 March: LHS 3844 b confirmed as the first tidally locked super-Earth exoplanet.
April 2024: Innovations
1 April: A new class of antibiotics targeting multi-drug-resistant bacteria was discovered, potentially revolutionizing infection treatment.
4 April: A study suggests global CO2 emissions increased by only 0.1% in 2023, indicating a potential plateau.
9 April: A rare genetic variation that reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer’s by over 70% is identified.
12 April: Researchers find that tardigrades’ biochemicals, especially Dsup protein, protect them from radiation exposure.
23 April: University of Maine presents the world’s largest 3D printer capable of printing large-scale objects.
26 April: mRNA-4157/V940, the first personalized melanoma vaccine based on mRNA, enters Phase III trials.
May 2024: The Cosmos and the Human Mind
1 May: The discovery of a brain circuit potentially acting as a “master regulator” of immunity linked the brain and immune system in groundbreaking ways.
5 May: The James Webb Space Telescope identified JADES-GS-z14-0, the most distant galaxy ever discovered, formed 290 million years after the Big Bang.
17 May – A team from the University of Bristol unveiled the world’s smallest quantum light detector, built on a silicon chip. This new version is 50 times smaller than their previous model.
24 May: Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences announced the successful tuning of the Casimir effect using magnetic fields.
31 May: Biologists have reported that Tmesipteris oblanceolata, a fern ally plant, contains the largest known genome.
June 2024: Space and Sustainability
2 June: China’s Chang’e 6 lunar mission successfully landed on the Moon’s far side, collecting valuable samples.
5 June: The Iberian lynx’s population surge led to its removal from the “endangered” list, showcasing conservation success.
11 June: Research suggests a link between serious kidney disease and human spaceflight.
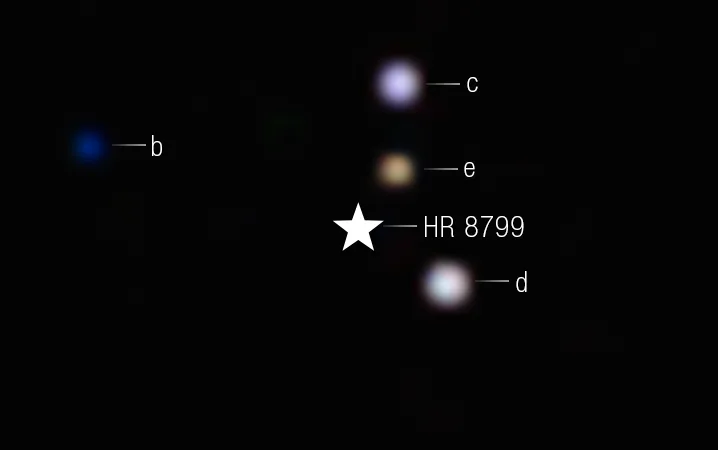
24 June: Three potentially habitable super-Earths were discovered around the star HD 48948, advancing the search for life beyond Earth.
July 2024: Climate and Dark Matter Insights
9 July: Rising sea levels caused the extinction of the Key Largo tree cactus, highlighting the dire effects of climate change.
11 July: The Hubble Telescope uncovered 3D velocity dispersion in a dwarf galaxy, offering deeper insights into dark matter distribution.
August 2024: Mars, mRNA
12 August: Liquid water was confirmed to exist 10–20 km below Mars’ surface, raising possibilities for future exploration and the search for life.
23 August: The first mRNA lung cancer vaccine, BNT116, began clinical trials, representing a major leap in cancer treatment.
September 2024: Quantum World and Climate Warnings
4 September: The European Space Agency’s BepiColombo spacecraft performed a record-setting 165 km flyby of Mercury. (Video)
11 September: A study conducted by Osaka University reveals that the bluestreak cleaner wrasse (Labroides dimidiatus), a small tropical fish, may exhibit a form of self-awareness.
23 September: A study forecasted the near-total collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet by 2300 if current trends continue.
October 2024: Technological Feats, Planetary Insights
2 October: Scientists completed the first-ever mapping of the entire brain of a fruit fly, revealing over 50 million connections between 139,000 neurons.
October 7: The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024 was awarded jointly to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun “for the discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation”
October 8: The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton for “for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks”.
9 October: AI-driven protein design led to the creation of enzymes capable of breaking down harmful industrial pollutants, offering a new tool for environmental cleanup.
9 October: The Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to David Baker “for computational protein design” and Demis Hassabis and John Jumper “for protein structure prediction”.
13 October: SpaceX achieved the first successful return and capture of a Super Heavy booster from Starship, setting a new benchmark in space technology.
18 October: Researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have introduced a holography-based computational technique that significantly enhances medical optical imaging.
23 October: Physicists from MIT and the Caltech have observed a “black hole triple” for the first time.
30 October: A new study on the infinite monkey theorem concludes that, even if all 200,000 chimpanzees on Earth typed one key per second, they would still fail to produce the complete works of Shakespeare before the universe’s end.
November 2024: AI and Health
15 November: Global measles cases have reportedly surged, with an estimated 10.3 million infections in 2023, marking a 20% increase compared to 2022.
21 November: The European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer has captured the first close-up image of a star beyond the Milky Way. The star, WOH G64, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud approximately 160,000 light-years away, is revealed to be encircled by a torus-shaped cloud.
December 2024: AI, Human Health
On December 5, researchers identified a single mutation, Q226L, that significantly enhances the ability of H5N1 (‘bird flu’) to infect human cells, particularly in the respiratory tract. Previously, it was believed that at least three mutations were necessary for the virus to infect and spread among humans.
On December 10, AI-based transfer learning models predicted that global warming could reach 3°C sooner than previously anticipated.
Welcoming 2025
In 2024, humanity took remarkable strides in science, whether it was unraveling the mysteries of space, advancing medical frontiers, or harnessing the transformative power of AI and technology. These breakthroughs remind us of the boundless potential of human curiosity and innovation.
At Everyman Science, we remain committed to delivering in-depth stories that decode complex topics, be it scientific, societal, or political. We hope this roundup of 2024’s major scientific achievements inspired you and deepened your appreciation for the incredible progress made this year.
Here’s to another year of discovery, wisdom, and scientific advancement. Bring on 2025!